> # REGRESSION DIAGNOSTICS
# Let's
change the folder to the one where we have data
> setwd("C:\Users\baron\627\data")
> load("Auto.rda")
> names(Auto)
[1] "mpg"
"cylinders"
"displacement"
[4] "horsepower"
"weight" "acceleration"
[7] "year"
"origin"
"name"
> attach(Auto)
> reg=lm(mpg
~ year + acceleration + horsepower + weight)
> par(mfrow=c(2,2))
> plot(reg)
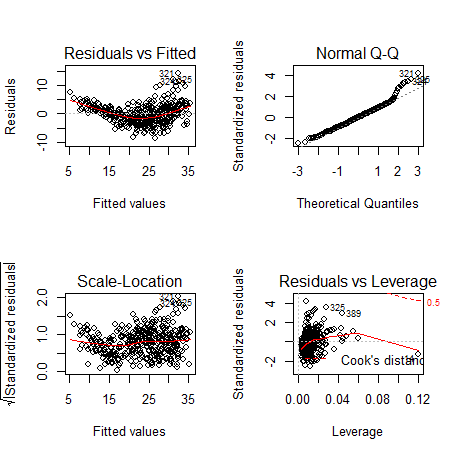
# STUDENTIZED RESIDUALS AND
OUTLIERS
> t = rstudent(reg)
> plot(t)
> t[ abs(t) > 3 ]
243
321 324 325
328 382
3.338459 4.272284
3.446234 3.651403 3.236226 3.024362
# Which of
these residuals can be considered as outliers?
# Compare with the Bonferroni-adjusted quantile from t-distribution.
> qt( 0.05/2/392, 387 )
[1] -3.870293
> t[ abs(t) > abs(qt( 0.05/392/2,
387 )) ]
321
4.272284
# Testing NORMALITY
> shapiro.test(t)
Shapiro-Wilk normality test
data: t
W = 0.97109,
p-value = 5.101e-07
# Also
look at the Normal Q-Q plot above. Shapiro-Wilk statistic W measures how close
the graph is to a straight line.
# Testing
HOMOSCEDASTICITY (constant variance). This is the Breausch-Pagan
test.
> ncvTest(reg)
Non-constant
Variance Score Test
Variance formula:
~ fitted.values
Chisquare = 22.04621
Df = 1 p = 2.66165e-06
# INFLUENTIAL DATA
> infl = influence(reg)
# Gives hat diagonals Hii, the vector of coefficients (without the ith case), s = RMSE (without the ith
case)
> leverage = infl$hat
> plot(leverage)
> 5/length(mpg)
[1] 0.0127551
> summary(infl$hat)
Min.
1st Qu.
Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
0.002781 0.007543
0.010640 0.012760 0.014740 0.120500
> leverage[ leverage > 0.03 ]
> infl$coefficients
> infl$sigma
# ADDITIONAL PACKAGE
"CAR" (Go to "Packages" tab and choose "car")
> library(car)
> outlierTest(reg)
rstudent
unadjusted p-value Bonferonni p
321 4.272284 2.4397e-05 0.0095635
> cook = cooks.distance(reg)
> plot(cook)
# The Cook’s distance measures the
effect of deleting the i-th observation
> influence.measures(reg)
# Besides the Cook’s distance, it
calculates DFBETS, DFFITS, and other measures of influence
# VARIANCE INFLATION FACTORS
> vif(reg)
year
acceleration horsepower weight
1.228910
2.519844 8.813443 5.303347